The store caters mostly to Windows 10 PCs, and using the MacOS filter doesn’t produce the platform’s entire Mac-compatible list. That makes the Epic Games Store library the best place to find. This location is likely to be referenced by an internal OS database, and I basically just had to hope that removing the file would allow the database to clear the entry and force the PKG file to download again. I deleted the file and restarted, asked iPhoto to install in the App Store, and everything went smoothly. If you see a bank app store screen or your app store app simply freezes or experiences interim crashing on macOS Catalina, check the following tips out. One trick that has worked in the past when dealing with odd behavior on the Mac app store is to change the System date/time. Now that Apple has release Mac OS X 10.15 Catalina, it is difficult to find and download Mojave on the Mac App Store. If you try to do a search for it, nothi. The App Store (also known as the Mac App Store) is a digital distribution platform for macOS apps, created and maintained by Apple Inc. The platform was announced on October 20, 2010, at Apple's 'Back to the Mac' event. Apple began accepting app submissions from registered developers on November 3, 2010, in preparation for its launch. Mac App Store was launched on January 6, 2011, as part of.
There are two basic ways that you, as an administrator, can deploy the OneDrive sync app to Mac users in your organization:
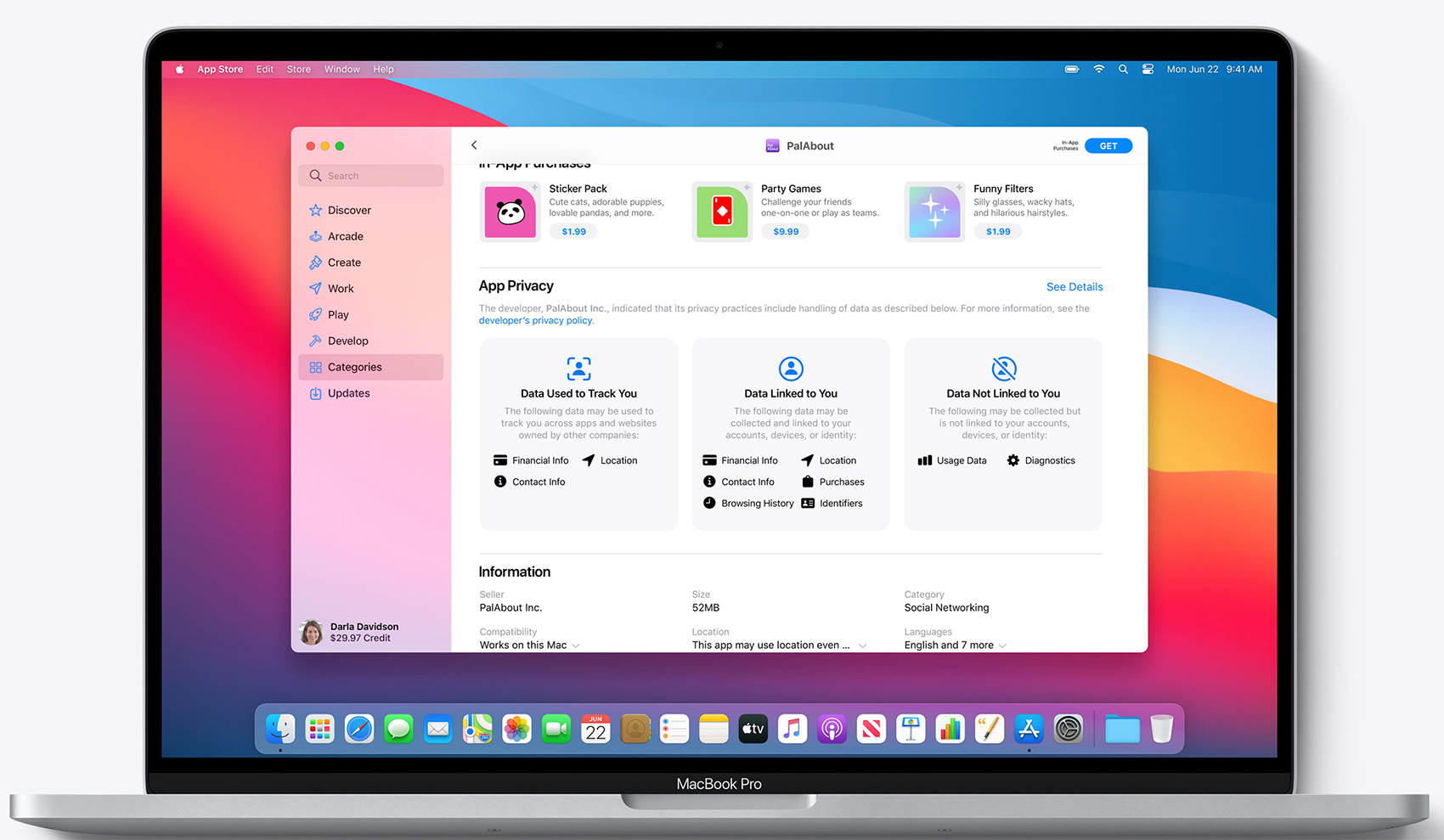
Have users install and set up the OneDrive sync app themselves by following the instructions in Sync files with OneDrive on Mac OS X. To install the OneDrive sync app for Mac, a user has to be an administrator on the Mac or know an administrator account name and password.
Download the installer package file to your local network, and then use your software distribution tools to deploy the app to your users. By using a software distribution tool, you have more control over the deployment, including which users get the sync app and when. The OneDrive sync app for Mac uses the Apple Installer technology for installation. This means you can continue to use the software distribution tools that you normally use to deploy software to Mac users. You can use Microsoft Intune. Other common tools are Jamf Pro, Munki, and AutoPkg. You can also use Apple Remote Desktop and AppleScript.
Manage OneDrive settings on macOS using property list (Plist) files
After the OneDrive sync app for Mac is installed, users can configure settings for the app. These settings are called preferences. As an administrator, you might want to provide users in your organization with a standard set of preferences. Preferences for the OneDrive sync app for Mac are stored in preference files. These files are often referred to as .plist files.
| Standalone | Mac App Store | |
|---|---|---|
| PList Location | ~/Library/Preferences/com.microsoft.OneDrive.plist | ~/Library/Containers/com.microsoft.OneDrive-mac/Data/Library/Preferences/com.microsoft.OneDrive-mac.plist |
| Domain | com.microsoft.OneDrive | com.microsoft.OneDrive-mac |
Configure sync app settings
Configure the settings on macOS as follows:
Quit the OneDrive app.
Define the settings you want to change by creating a Plist file with the values, or use a script to set the default values.
Deploy the settings onto the local computer.
Refresh the preferences cache.
On the next start of OneDrive, the new settings will be picked up.
Overview of settings
Use the following keys to preconfigure or change settings for your users. The keys are the same whether you run the standalone or Mac App Store edition of the sync app, but the Plist file name and domain name will be different. When you apply the settings, ensure that you target the appropriate domain depending on the edition of the sync app.
List of settings
AllowTenantList
This setting prevents the users from uploading files to other organizations by specifying a list of allowed tenant IDs. If you enable this setting, the user gets an error if they attempt to add an account from an organization that is not in the allowed tenants list. If the user has already added the account, the files stop syncing. This setting takes priority over Block syncing OneDrive accounts for specific organizations setting. Do NOT enable both settings at the same time.
The parameter for the AllowTenantList key is TenantID and its value is a string which determines the tenants for whom the Allow Tenant setting is applicable. For the setting to be complete, this parameter also requires a boolean value to be set to it. If the boolean value is set to True, the tenant is allowed to sync.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>AllowTenantList</key>
<array>
<dict>
<key>TenantId1</key>
<Bool>True</Bool>
<key>TenantId2</key>
<Bool>True</Bool>
</dict>
</array>
AutomaticUploadBandwidthPercentage
This setting enables the sync app to automatically set the amount of bandwidth that can be used for uploading files, based on available bandwidth.
To enable this setting, you must define a number between 1 and 99 which determines the percentage of bandwidth the sync app can use out of the total available bandwidth.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>AutomaticUploadBandwidthPercentage</key>
<int>(Bandwidth)</int>
BlockExternalSync
This setting prevents the sync app from syncing libraries and folders shared from other organizations.
If you set the setting's value to True, the users are prevented from syncing OneDrive and SharePoint libraries and folders with organizations other than the user's own organization. Set this value to False or do not enable the setting to allow the OneDrive and SharePoint files to be synced with other organizations also.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>BlockExternalSync</key>
<(Bool)/>
BlockTenantList
This setting prevents the users from uploading files to organizations that are included in the blocked tenant IDs list that is specified.

If you enable this setting, the users get an error if they attempt to add an account from an organization that is blocked. If a user has already added an account for a blocked organization, the files stop syncing. This setting does NOT work if you have Allow syncing OneDrive accounts for only specific organizations setting enabled. Do NOT enable both settings at the same time.
You must enable this setting by defining IDs for the TenantID parameter which determines the tenants to whom the block tenant setting is applicable. You must also set the boolean value to True for the ID of every tenant you want to prevent from syncing with the OneDrive and SharePoint files and folders.
Note: In the list, inclusion of the tenant ID alone does not suffice. It is mandatory to set the boolean value to True for the ID of each tenant who is to be blocked.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>BlockTenantList</key>
<array>
<dict>
<key>TenantId1</key>
<Bool>True</Bool>
<key>TenantId2</key>
<Bool>True</Bool>
</dict>
</array>
DefaultFolderLocation
This setting specifies the default location of the OneDrive folder for each organization.
The parameters are TenantID and DefaultFolderPath.The TenantID value is a string that determines the tenants to whom the default folder location setting is applicable.The DefaultFolderPath value is a string that specifies the default location of the folder.
The following are the conditions governing the default folder location:-Mac app store: The path must already exist when the user is setting up the sync app.-Standalone: The path will be created (if it doesn't already exist) after the user sets up the sync app. Only with the Standalone sync app you can prevent users from changing the location.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>DefaultFolder</key>
<array>
<dict>
<key>Path</key>
<string>(DefaultFolderPath)</string>
<key>TenantId</key>
<string>(TenantID)</string>
</dict>
</array>
DisableHydrationToast
This setting prevents toasts from appearing when applications cause file contents to be downloaded.
If you set the setting's value to True, toasts do not appear when applications trigger the download of file contents.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>DisableHydrationToast</key>
<(Bool)/>
DisablePersonalSync
This setting blocks users from signing in and syncing files in personal OneDrive accounts. If this setting has been configured after a user has set up sync with a personal account, the user gets signed out.
If you set the setting's value to True, the users are prevented from adding or syncing personal accounts.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>DisablePersonalSync</key>
<(Bool)/>
DisableTutorial
This setting prevents the tutorial from being shown to the users after they set up OneDrive.
If you set this setting's value to True, the tutorial is blocked from being shown to the users after they set up the OneDrive.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>DisableTutorial</key>
<(Bool)/>
DownloadBandwidthLimited
This setting sets the maximum download throughput rate in kilobytes (KB)/sec for computers running the OneDrive sync app.
You must set this setting's value to an integer between 50 KB/sec and the maximum rate is 100,000 KB/sec which determines the download throughput in KB/sec which the sync app can use.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>DownloadBandwidthLimited</key>
<int>(Download Throughput Rate in KB/sec)</int>
FilesOnDemandEnabled
This setting specifies whether Files On-Demand is enabled.
If you don't set this setting, Files On-Demand will be enabled automatically as we roll out the feature, and users can turn the setting on or off.
If you set this setting to True, FilesOnDemand is enabled and the users who set up the sync app can view the online-only files, by default.
If you set this setting to False, FilesOnDemand is disabled and the users won't be able to turn it on.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>FilesOnDemandEnabled</key>
<(Bool)/>
HideDockIcon
This setting specifies whether a dock icon for OneDrive is shown.
If you set this setting's value to True, the OneDrive dock icon is hidden even if the app is running.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>HideDockIcon</key>
<(Bool)/>
HydrationDisallowedApps
This setting prevents apps from automatically downloading online-only files. You can use this setting to lock down apps that don't work correctly with your deployment of Files On-Demand.
To enable this setting, you must define a string in JSON format as described below:[{'ApplicationId':'appId','MaxBundleVersion':'1.1','MaxBuildVersion':'1.0'}]
'appID' can be either the BSD process name or the bundle display name. 'MaxBuildVersion' denotes the maximum build version of the app that will be blocked. 'MaxBundleVersion' denotes the maximum bundle version of the app that will be blocked.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>HydrationDisallowedApps </key>
<string> [{'ApplicationId':'appId','MaxBundleVersion':'1.1','MaxBuildVersion':'1.0'}, {'ApplicationId':'appId2','MaxBundleVersion':'3.2','MaxBuildVersion':'2.0'}]</string>
<(Bool)/>
OpenAtLogin
This setting specifies whether OneDrive starts automatically when the user logs in.
If you set this setting's value to True, OneDrive starts automatically when the user logs in on Mac.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>OpenAtLogin</key>
<(Bool)/>
SharePointOnPremFrontDoorUrl

This setting specifies the SharePoint Server 2019 on-premises URL that the OneDrive sync app must try to authenticate and sync against.
To enable this setting, you must define a string containing the URL of the on-premises SharePoint Server.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>SharePointOnPremFrontDoorUrl</key>
<string>https://Contoso.SharePoint.com</string>
SharePointOnPremPrioritizationPolicy
This setting determines whether or not the client should set up sync for SharePoint Server or SharePoint in Microsoft 365 first during the first-run scenario when the email is the same for both SharePoint Server on-premises and SharePoint in Microsoft 365 in a hybrid scenario.
If you set this setting's value to 1, it is an indication that OneDrive should set up SharePoint Server on-premises first, followed by SharePoint in Microsoft 365.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>SharePointOnPremPrioritizationPolicy</key>
<int>(0 or 1)</int>
SharePointOnPremTenantName
This setting enables you to specify the name of the folder created for syncing the SharePoint Server 2019 files specified in the Front Door URL.
If this setting is enabled, you can specify a TenantName which is the name the folder will use in the following convention:
OneDrive – TenantName (specified by you)
TenantName (specified by you)
If you do not specify any TenantName, the folder will use the first segment of the FrontDoorURL as the its name. For example, https://Contoso.SharePoint.com will use Contoso as the Tenant Name in the following convention:
OneDrive – Contoso
Contoso
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>SharePointOnPremTenantName</key>
<string>Contoso</string>
UploadBandwidthLimited
This setting defines the maximum upload throughput rate in KB/sec for computers running the OneDrive sync app.
To enable this setting, set a value between 50 and 100,000 which is the upload throughput rate the sync app can use.
The example for this setting in the .plist file is:
<key>UploadBandwidthLimited</key>
<int>(Upload Throughput Rate in KB/sec)</int>
You can also configure the OneDrive Standalone sync app to receive delayed updates.
| PList Location | Domain |
|---|---|
| ~/Library/Preferences/com.microsoft.OneDriveUpdater.plist | com.microsoft.OneDriveUpdater |
| Setting | Description | Parameters | Example Plist Entry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier | Defines the update ring for the computer | UpdateRing (String): This parameter has two different values. Production - The default update ring for OneDrive updates. Insiders - This update ring receives updates that are 'pre-production' and that allow you to play with features before they are released. Note that builds from this ring may be less stable. Enterprise - This update ring (now called 'Deferred') receives updates after they have been rolled out through the Production ring. It also lets you control the deployment of updates. For more information about the update rings and the procedure used by the sync app for checking for updates, see The OneDrive sync app update process. | <key>Tier</key> <string>(UpdateRing)</string> |
Starting with OS X Mountain Lion, Apple introduced Gatekeeper so users couldn’t easily install downloaded apps from outside the Mac App Store.
When someone downloads an app from somewhere other than the Mac App Store they will get one of a few warning messages depending on what security settings they’ve set in System Preferences. We’ll show users how to set the security settings in Security & Privacy section of the OS X System Preferences using any version of OS X after Mountain Lion so they can install downloaded apps from outside the Mac App Store.
Why Can’t I Install 3rd-Party Apps By Default?
If you don’t care about why this works, skip to the next section. Here’s why Apple sets OS X to disallow 3rd-party apps by default, for those who like to understand why things work as they do.
Cynics will say that Apple does this because they don’t get a 30% cut from applications bought directly from third-party apps instead of their curated app store. A $10 app nets Apple $3 and the developer gets only $7. The developer gets the entire $10 if the app is sold directly.
Apple says they set things blocking third-party apps because they want to protect users who might install downloaded apps with malware or viruses. They take the 30% cut to cover the cost of hosting the Mac App Store and testing apps to keep malware out of the store. In other words, they want to help protect us from our own mistakes.
Apple offers three setting options in the Security & Privacy Settings in System Preferences. Apple set the default to help protect users from Malware or to lock down computers depending on which explanation you prefer.
Apple created Gatekeeper, a program to protect users from Malware. Developers can get a security certificate from Apple through the Apple Developer program. If a developer distributes their app on the Mac App Store, they have to follow certain guidelines to get approved. These guidelines try to keep malware out of the store. Developers can also add a security certificate to their apps. The certificate is some code inserted into the app code. Users can set their machines to allow third-party apps downloaded from the Internet, but only if they include one of these security certificates.
Find out how to change the settings below so you can install downloaded apps from trusted third-party websites. Don’t install apps from just any site because relaxing security settings could potentially open the door to malware and viruses.
How to Install Apps from Outside the Mac App Store
To install third-party apps, the user must change a setting in the Security & Privacy section of System Preferences, the Settings app in OS X.
Open OS X System Preferences by clicking on the app icon from OS X Dock or by clicking the Apple icon in the Menu Bar in the upper left corner of the screen. When the menu pops up, click on System Preferences.
Click on Security & Privacy from the top row of the System Preferences app. Choose the General tab to see the settings below.
There’s a lock icon at the bottom of the dialog box. Click it to enable all the settings in the box. The OS will ask the user to enter their administrator’s password. Click OK and the grayed out settings become clickable.
The settings we need to work with show up at the bottom half of the dialog box. There are three options under Allow apps downloaded from:. Here are the descriptions taken from Apple’s support site.
- Mac App Store – Only apps that came from the Mac App Store can open.
- Mac App Store and identified developers (default in OS X) – Only allow apps that came from the Mac App Store and developers using Gatekeeper can open.
- Anywhere – Allow applications to run regardless of their source on the Internet (default in OS X Lion v10.7.5); Gatekeeper is effectively turned off. Note: Developer ID-signed apps that have been inappropriately altered will not open, even with this option selected.
If the user chooses the first two options, they can close the dialog box and continue. However, if the user chooses Anywhere, the above warning pops up to scare the user from using this setting. It says:
Choosing “Anywhere” makes your Mac less secure.
The warning box explains that OS X resets this setting after 30 days. Users will have to come back here and do the above steps again. Further, it explains that it’s safer to let the OS warn you each time you launch an app, which includes an option to allow it by clicking an OK button if you select the middle option of the three.
Which Option Should You Choose?
Those who only install apps from the Mac App Store should not bother changing the default settings. Make sure to select the first option labelled Mac App Store and close the box. If you want to install and run any app you want and don’t worry at all about malware, then choose the third option labelled Anywhere. I use the second option since I can still install third-party apps, but they have to come from developers who take the time to add an Apple Developer security certificate to their app. These are safe, but can come from outside the Mac App Store.
Related Posts
Among Us
While most people can access their email via the web these days, having a dedicated…
We've put together a list of some of the best Mac apps anywhere: if you're looking…
Any time a user installs a new application on a Mac, it becomes the default…



